- checks out bbmagic_lib library compatibility using bbm_bt_lib_version() function
- turns on BBMagic Bluetooth communication using bbm_bt_open(..) function
- receives data from BBMagic MAGNETO module using bbm_bt_read(..) function
- displays all these information on the screen
- ends when ‘ctrl+c’ is pressed and closes BBMagic Bluetooth communication using bbm_bt_close() function
Application files
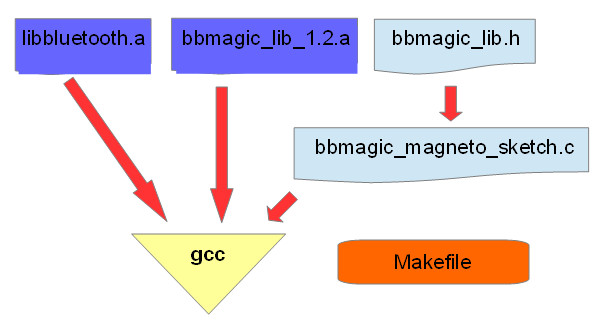
- bbmagic_lib_1.2.a – it is library for receiving data from BBMagic devices through Bluetooth Low Energy radio link. It’s for Raspberry Pi zero W and Raspberry Pi 3 which have Bluetooth LE chipset onboard.
- bbmagic_lib.h – it is bbmagic_lib header file containing definitions and constants
- libbluetooth.a – it is library from libbluetooth-dev Debian package that contains development files for using the BlueZ Linux Bluetooth library.
- bbmagic_magneto_sketch.c – it is our main application ‘C’ file
- Makefile – it contains compilation instructions for make program
Project preparation
Make new directory for our project on your Raspberry Pi: mkdir bbmagic_magneto_sketch
and go to it:cd bbmagic_magneto_sketch
Open your favorite file editor and if you have not one try nano – its simple and intuitive:nano bbmagic_magneto_sketch.c
Writing app for BBMagic MAGNETO
1. Include header files required and put main function#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include "bbmagic_lib.h"
int main(void)
{
2. Variables declarationsunsigned char bbm_buf[BBLIB_FRAME_SIZE] ;
int i, data_length ;
float vcc_f, adc_1, adc_2 ;
- bbm_buf – buffer for BBMagic MAGNETO sensor data. Its size ‘BBLIB_FRAME_SIZE’ is defined in ‘bbmagic_lib.h’ file
- vcc_f – contains BBMagic MAGNETO power supply voltage
- adc_1, adc_2 – for samples from ADC_1 and ADC_2 input
- i, data_length – needs for … you will see below 🙂
3. Checking out bbmagic_lib library version
If this is 0x0102 version its ok – our app can play with it.
i = bbm_bt_lib_version() ;
printf("bbm_lib_version: %0.4X - ",i) ;
if(i == 0x0102) printf("ok\n") ;
else
{
printf("nok - stop\n\n") ;
exit(1) ;
}
4. Turn on BBMagic Bluetooth communication
i = bbm_bt_open(17) ;
if(i) exit(2) ;
THe bbm_bt_open(..) function gets pin number with LED connected. It indicates BBMagic Bluetooth transfer. Pin number should be in range from 1 to 27. If out of this range BBMagic Bluetooth transmission indication is off.
You can connect LED in two different ways:
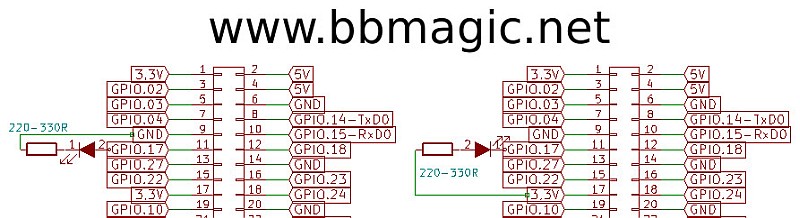
do
{
data_length = bbm_bt_read(bbm_buf) ;
if(data_length > 0)
{
If data arrives it is in ‘bbm_buf’ buffer.
- data_length > 0 : received ‘data_length’ bytes of data from BBMagic sensor
- data_length == 0 : there is no data received
- data_length == -1 : user break by ‘ctrl+c’
- data_length == -10 : BBMagic data authentication error
All possible returned values are defined in ‘bbmagic_lib.h’ file.
6. Is received data from BBMagic MAGNETO?
switch(bbm_buf[BBMAGIC_DEVICE_TYPE])
{
case BBMAGIC_M_MAGNETO :
Constants ‘BBMAGIC_DEVICE_TYPE’ and ‘BBMAGIC_M_MAGNETO’ are defined in ‘bbmagic_lib.h’ file.
7. Calculating and displaying all the information from BBMagic MAGNETO
- Display module name:
printf("BBM_MAGNETO_") ; - And then six bytes of module Bluetooth address
for(i=0; i<BBM_BT_ADDR_SIZE; i++)
printf("%0.2X", bbm_buf[BBMAGIC_DEVICE_ADDR_5 + i]) ; - BBMagic MAGNETO firmware version:
printf(" | firm_version:%0.2X.%0.2X\n", bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_FIRM_1], bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_FIRM_0]) ; - Calculate and display module supply voltage
vcc_f = bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_V_SUP] ; vcc_f/=BBMAGIC_VCC_DIVIDER ;
printf(" chip_vcc:%0.2fV", vcc_f) ;
- BBMagic MAGNETO chip temperature:
printf(" | chip_temp:%d*C", (signed char)bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_CHIP_TEMP]) ; - Show module working time from power up (in seconds)
i =bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_WORKTIME_3] ; i<<=8 ;
i |=bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_WORKTIME_2] ; i<<=8 ;
i |=bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_WORKTIME_1] ; i<<=8 ;
i |=bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_WORKTIME_0] ;
printf(" | chip_working:%4d s",i) ;
- Display radio signal strength
printf(" | RSSI:%ddBm", (signed char)bbm_buf[BBMAGIC_DEVICE_RSSI]) ;
- ADC_1 and ADC_2 inputs voltage
adc_1 =bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_ADC_1_MSB] ; adc_1 *=256.0 ; adc_1 +=bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_ADC_1_LSB] ; adc_1 /=1000.0 ;
adc_2 =bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_ADC_2_MSB] ; adc_2 *=256.0 ; adc_2 +=bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_ADC_2_LSB] ; adc_2 /=1000.0 ;
printf(" ADC_1: %1.2fV | ADC_2: %1.2fV", adc_1, adc_2) ;
- Light level
printf(" | Light: %d", bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_LIGHT]) ;
8. Check out presence of magnetic field
if(bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_FLAGS] & BBM_MAGNETO_MAGNET_MASK)
printf(" | MAGNET detected") ;
else printf(" | no MAGNET") ;
‘BBM_MAGNETO_FLAGS’ and ‘BBM_MAGNETO_MAGNET_MASK’ constants are defined in ‘bbmagic_lib.h’ file of course.
9. Check out IN_0 to IN_3 input state.
if(bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_FLAGS] & BBM_MAGNETO_IN_0_BIT)
printf("\n IN_0 - LO") ;
else printf("\n IN_0 - HI") ;
if(bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_FLAGS] & BBM_MAGNETO_IN_1_BIT)
printf(" | IN_2 - LO") ;
else printf(" | IN_1 - HI") ;
if(bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_FLAGS] & BBM_MAGNETO_IN_3_BIT)
printf(" | IN_3 - LO") ;
else printf(" | IN_2 - HI") ;
if(bbm_buf[BBM_MAGNETO_FLAGS] & BBM_MAGNETO_IN_3_BIT)
printf(" | IN_4 - LO") ;
else printf(" | IN_3 - HI") ;
break ;
10. Close ‘switch’ statement
If there is received data from other BBMagic sensor lets show its address and type.
default:
printf("BBM_UNKNOWN_") ;
for(i=0; i<BBM_BT_ADDR_SIZE; i++)
{
printf("%0.2X", bbm_buf[BBMAGIC_DEVICE_ADDR_5 + i]) ;
}
printf(" BBM_TYPE=%0.2X", bbm_buf[BBMAGIC_DEVICE_TYPE]) ;
break ;
} ;
11. Close ‘if(data_length > 0)’ statement
printf("\n") ;
}
12. Close ‘do{‘ statement
Wait 100 microseconds and do receive loop again untill ‘ctrl+c’ is pressed (bbm_bt_read(..) function returns -1).
usleep(100) ;
}while(data_length != -1) ;
13. Close BBMagic Bluetooth communication
If ‘ctrl+c’ pressed the program ends.
bbm_bt_close() ;
exit(0) ;
}
And its finished !!
Press ‘ctrl+X’ then ‘Y’ and hit ‘Enter’ to save bbmagic_magneto_sketch.c file.

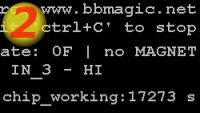
After compilaton you can run application and get on the screen something like this: